Road Management
As of April 1, 2013, the total length of the road network in the Tokyo Metropolis was approximately 24,431 km (of which approximately 2,347 km is administered by the Tokyo Metropolitan Government). The network occupies an area measuring approximately 184.67 sq km. (of which TMG administered roads account for approximately 44.83 sq km).
The Bureau’s duties with respect to road management include administrative procedures set forth by the Road Act (determination of road name and route, including the start and end points; determination of road jurisdiction which specifically establishes the responsibility held by the administrator for road maintenance and management; changes to road jurisdiction), and permit issuance (special permits for vehicles that exceed set standards such as vehicle width or weight, road occupancy permits for lifeline utilities, including electric, gas, water and sewer, and telephone lines, that continuously occupy the road). In addition, tasks include coordinating with other agencies for guidance and enforcement with respect to improper road use, road surface maintenance and repair, development and maintenance of road facilities, creation of space for bicycles, and projects to improve the roadside environment. The Bureau continues to move forward with these tasks, while aiming to protect the living environment and harmony of communities.
Furthermore, the Bureau is studying the possibility of installing equipment that utilizes ubiquitous technology to support effective maintenance and management of roads that run underground.
The 2011 Great East Japan Earthquake created a new awareness of the importance of the role that roads play in such areas as the transport of relief supplies and recovery operations following a disaster. In order to ensure that emergency transport roads are functional when a major earthquake strikes, the Bureau is actively pursuing initiatives outlined in the Tokyo Vision 2020 plan, including the seismic retrofitting of bridges and the elimination of utility poles by moving power lines underground.
Status of roads in Tokyo (as of April 1, 2013)
| Area | Land area (km2) |
Length of roads (km) |
Area occupied by roads (km2) |
Road-to-land ratio (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wards | 622.99 | 11,870 | 101.786 | 16.3 |
| Tama District | 1,159.90 | 11,082 | 75.766 | 6.5 |
| Islands | 405.78 | 1,479 | 7.122 | 1.8 |
| Total | 2,188.67 | 24,431 | 184.674 | 8.4 |
Main facilities occupying roads
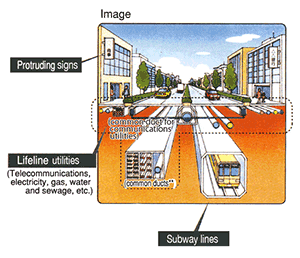
(Common duct**)
** Common ducts are structures that effectively organize and consolidate underground utility lines, including electric, gas, and water, ensuring these lines are securely protected. The creation of common ducts will facilitate better control with respect to digging up streets, as well as have a large impact on urban disaster resistance.




